What is the ISPS Code?
ISPS or the International Ship and Port Facility Security Code is an substantive nautical regulation for the safety and security system of ships, ports, cargo and crew .
The biggest challenge the world is facing today is fighting terrorism. There have been many events in the history recently involving terrorist attacks in different parts of the earth in different forms .
But the most ghastly of all – September 11 terrorist attack on the gemini towers ( World Trade Centre ) proved that the national and international security was on stake .
The maritime security is a prevail issue and respective incidences have taken place even before the 9/11 attack ( for e.g. On 26th February 2000, bombs that were hidden inside two crowded buses in a Philippians ’ ferry – Our lady of Mediatrix, exploded and killed 45 passengers ).
Before the ISPS code, the SOLAS primary focus was the base hit of the ship at ocean. As security and condom are entirely different topics, newly amendments were made in SOLAS and the Chapter XI, which contains measures to enhance nautical safety, by renaming to Chapter XI-1 and a new Chapter XI-2 was added with extra focus on maritime security .
Related Read: SOLAS and MARPOL – A General Overview
This raw chapter comprises of regulations known as International Code for the Security of Ships and of Port Facilities with the abbreviated name “ International Ship and Port Facility Security Code or the ISPS Code ” .
Since the ocean is one of the easiest ways to approach an international territory, International Maritime Organisation ( IMO ) under SOLAS convention chapter XI-2 developed the International Ship and Port Facility Security code – The ISPS code for the base hit of ships, ports, seafarers and government agencies .

The ISPS code was implemented by IMO on July 1st 2004 as a comprehensive examination arrange of measurements for external security by prescribing responsibilities to a government authority, port assurance, shipping companies and seafarers .
It applies to the ships doing external voyages which include passenger ships & cargo ships of 500 GT and above .
Related Read: 10 Ways to Enhance Ship Security
Main Aim of ISPS code In Shipping
The ISPS code chiefly looks after the security aspects of the ship, seafarers, ports and port workers, to ensure preventive measures can be taken if a security threat is determined. The independent purpose of the International Code for the Security of Ships and of Port Facilities ( ISPS ) is as follows :
- To monitor the activity of people and cargo operation
- To detect the different security threats onboard vessel and in port and implement the measure as per the situation
- To provide a security level to the ship and derive various duties and functions at the different security level
- To establish the respective roles and responsibilities of the contracting governments, agencies, local administrations and the shipping and port industries
- To build and implement roles and responsibilities for port state officer and onboard officers to tackle maritime security threat at the international level
- To collect data from all over the maritime industry concerning security threats and implementing ways to tackle the same
- To ensure the exchange of collected security-related information data with worldwide port and ship owners network
- To provide a methodology for security assessments so as to have in place plans and procedures to react to changing security levels
- To find the shortcomings in the ship security and port security plan and measure to improve them
Related Read: Measures Taken During Shipboard Operation for the Safety of Ship ’ second Crew, Cargo, and Marine Environment
ISPS Code Requirements
The ISPS code incorporates assorted functional requirements so that it can achieve certain objectives to ensure the security of ships and ports. Some of the crucial requirements are as follows :
- To gather the security-related information from the contracting government agencies
- To assess the received information
- To distribute the security-related information to appropriate contracting government agencies
- Defining the proper communication protocols for ships and port facilities for hassle-free information exchange
- To prevent any unauthorised entry in port facilities or on a ship and other related restricted areas, even if the unauthorised entry is not a threat (but always considered as a potential threat)
- To prevent the passage of unauthorised weapons, incendiary devices or explosives to ships and port facilities
- To provide different means for raising the alarm if any security incident is encountered or a potential security threat is assessed
- To implement proper security plan on port and ship-based upon the security assessment and requirements
- To plan and implement training, drills and exercises for ship and port crew so that they are familiar with the security plans and there is no delay in implementing the same in case of a real threat
Related Read: What are the Duties of the Contracting Government ( CG ) under the ISPS Code ?
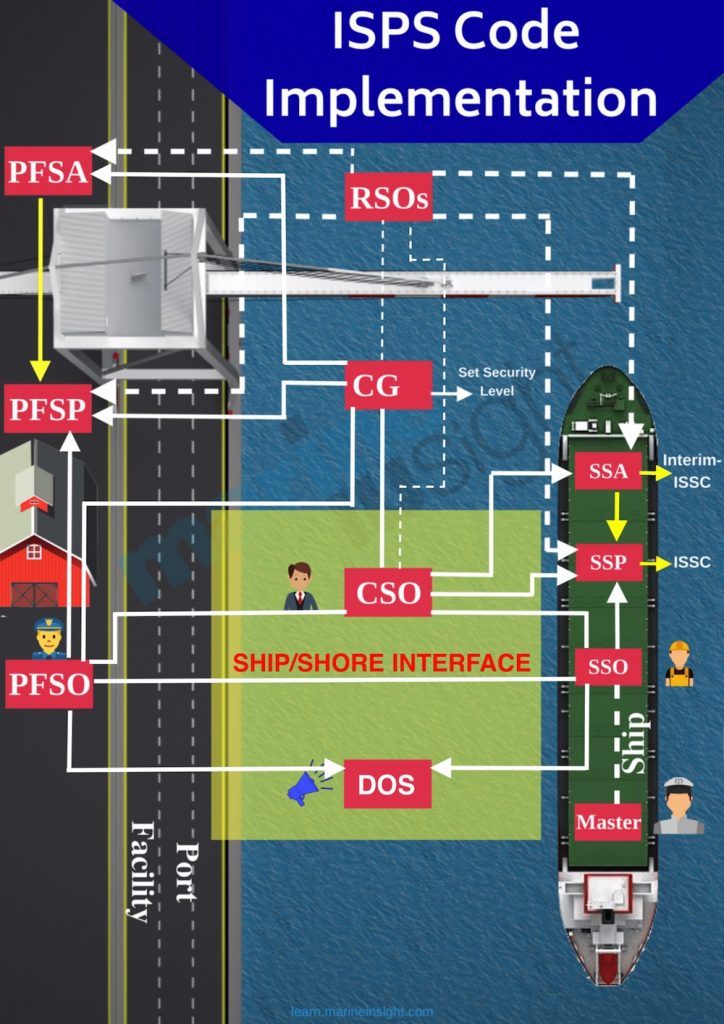
ISPS Code Meaning for Ships:
The cargo ships are vulnerable to security threats as they barely carry any weapon of security in case of a veridical attack. Piracy, terrorist attack, stowaways etc. are real-time threats haunting the ship and its crew. Improved ship security will be required in order to identify and take hindrance measures against such security incidents .
The administration is responsible for reviewing and approving a transport security plan for the ship, which will besides include any amendments of old plans etc .
The company must train its officeholder for ship security officer authentication and the judgment of the transport security will be carried onboard by these certify officers only. The seasonably judgment of the ship security plan ( SSP ) by a certifiable policeman is essential for finding shortcomings and enhancing the current SSP .
The ship security judgment shall be documented, reviewed, accepted and retained by the company. Every ship must carry an approved ship security plan approved by the Administration .
ISPS Code for Vessels Includes :
Company Security Officer ( CSO )
CSO is a company appointed person, who is creditworthy for the ship security assessment and for the onboard review to confirm the development and implementation of the transport security plan as per ISPS code. If any lack occurs, CSO is responsible to deal with all the non-conformities and to modify SSP as per the insufficiency .
Related Read: What are the Duties of Ship ’ s Company Security Officer ( CSO ) ?
Ship Security Officer ( SSO )
SSO is the i- charge of security of the vessel onboard and creditworthy for the other entire crowd extremity to carry out duties for ship security system as per ISPS code. SSO is responsible for carrying out frequent drills for ISPS Code as per SSP .
Related Read: What Are The Duties Of Ship Security Officer ( SSO ) ?
Ship Security Plan ( SSP )
Read more: A Man Quotes Maritime Law To Avoid Ticket
It is a plan kept onboard vessel mentioning the duty of crowd members at different security levels and the do ’ south and don ’ triiodothyronine at a different type of security threats. SSO is responsible under CSO to implement ship security design onboard vessel .
Related Read: Understanding Ship Security Plan On Board Ships
Ship Security Alert System
Different types of security equipment are kept onboard which includes a metallic detector for checking the person entering the vessel. From July 2004, most of the embark has installed the Ship Security Alert System ( SSAS ) as per ISPS norms which do not sound on the ship but alarm the shore agency about the security menace .
Related Read: What is ship Security Alert System ( SSAS ) ?
Implementing ISPS Security Level
It ’ s the duty of SSO to implement the security level onboard complying with the security horizontal surface set by the local anesthetic government authorities. besides, a continuous answer is to be made to Port state when the security level is “ level 3 ” .
ISPS Code for Port Facilities
interface facilities have to make certain that all the facilities are protected from any kind of threats which may arise from both land and body of water. They besides need to monitor the ships which are coming to its shore from an international voyage for any security risk .
It is the interface facility which defines the security levels to be implemented on the ships which are in its territorial waters. The Port wield company is responsible for preparing the Port Facility Security Plan .
The port facilities security appraisal is besides an essential and integral part of the process of developing and updating the port facility security plan .
The assessment is normally assessed and reviewed by the flag submit or by the government organization responsible for shipping and larboard development for that nation .
ISPS Code for Port Facilities Includes:
Port Facility Security Officer ( PFSO )
PFSO is a Government-appointed officer creditworthy for implementing PFSP and to derive security levels for port and vessel berth at their breakwater. He is responsible to conduct a port facility security assessment .
Port Facility Security Plan ( PFSP )
It includes the plans and action to be taken at different security levels. Roles and responsibilities are included in PFSP. military action to be taken at the time of any security breach is described in PFSP .
Related Read: The Importance of Port Security
Security Equipment
Minimum security system equipment like scanner and metal detector etc. must be available at all times with the interface facility to avoid the transgress of security inside the port .
Implementing Security Level
security levels are implemented by the port agency under the consultation of a local politics authority. The security flat adopted for the larboard facility must be informed to vessel administration for cooperative measures .
Challenges of ISPS code:
Every regulation comes with its own challenges. The ISPS code is no different and has the follow concerns :
- Human rights are one of the biggest concerns with ISPS code as it directly affects the seafarers’ wellbeing. Shore leave has always been considered as an essential stress relief process for the ship’s crew, and due to the security threats many countries are prohibiting shore leave for seafarers
Related Read: Everything You ever Wanted to know about ‘ Shore Leave
- Proper implementation of ISPS code is another concern as not all the crew are trained at the shore for ship security training.
- It also impacts on the daily activity of crew as it comes with additional duties of security watch etc.
- Implementing the security level on the ship is also an additional job, which is time-consuming.
- The port activities are also affected when the security level rises, leading to slow down of cargo operation
- When the security level is at its highest level, the port stay of the ship will increase as all the cargoes are checked as compared to lower security level (1 & 2), wherein only a handful of cargoes are inspected for security reasons
- Some ports do not allow any cargo operations under security level 3 until the level is minimised.
Advantages of ISPS Code:
- The ISPS aims to increase the safety and security of the ship hence minimised the risk
- Better control of cargo flow, personal access
- Better documentation procedure (as it has standard procedures all over)
- Secured working environment making it easier for seafarers and port workers
Disadvantages of ISPS:
- Additional work for seafarers as more security-related tasks are added to the work routine
- Slow work progress when the security level rises
- Additional paperwork and certification requirements
- Increase in operating cost of the ship for ISPS implementation and increase in port costs (more port stay) if the security level is higher
- More administration work
Related Read:
References International Maritime Organisation
Disclaimer: The authors ’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The generator and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any duty for the lapp. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any run of legal action to be followed by the subscriber .
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
